Respiratory Therapist’s Role in Tracheostomy

Respiratory therapists play a crucial role in airway management including tracheostomy and mechanical ventilation management. Ideally, RTs work as part of an interdisciplinary team to manage patients with tracheostomy. Although the role can vary, RTs have specialized knowledge in the respiratory system to provide key insight into tracheostomy management.
Respiratory therapists do not perform the surgery for tracheostomy tube placement, but may be involved in helping to ventilate the patient during the procedure, providing input such as the appropriate size and type of the tracheostomy tube, and setting up equipment. Once the tube is in place, respiratory therapists may be the main clinician involved in tracheostomy care.
Respiratory Therapy and Tracheostomy Care
Respiratory therapists who are involved in tracheostomy care will likely be involved in making sure all emergency equipment is at the bedside. The are also involved in minimizing bronchial secretions such as through suctioning. Their role in minimizing secretions includes the use of chest clearance exercises and breathing techniques as well as respiratory muscle strength training. Insufflation/exsufflation devices can also be used. Pharmacologic therapies may also be considered and administered by RTs to help improve mobilization of secretions. Respiratory therapists play a role in reducing ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP) by helping to mobilize and remove the patient’s secretions. VAP affects between 9% and 27% of all ventilated patients with associated mortality estimates between 33% and 50% (Kalanuria, AA et al, 2014).
Intermittent positive pressure breathing devices can improve lung volumes and decrease the work of breathing. The American Association for Respiratory Care (AARC) recommends the use only for patients with atelectasis and suggests the effects of IPPB are short term.
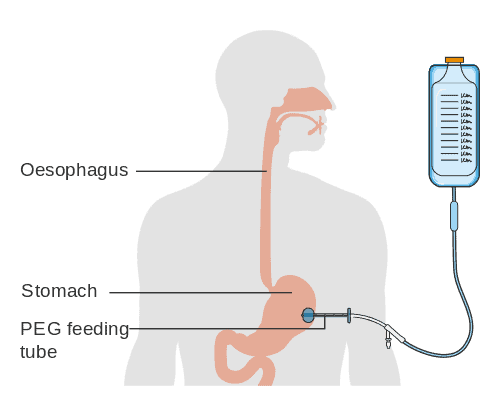
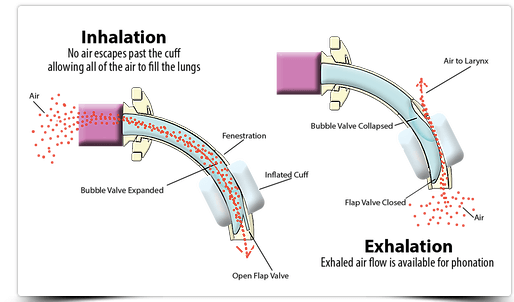
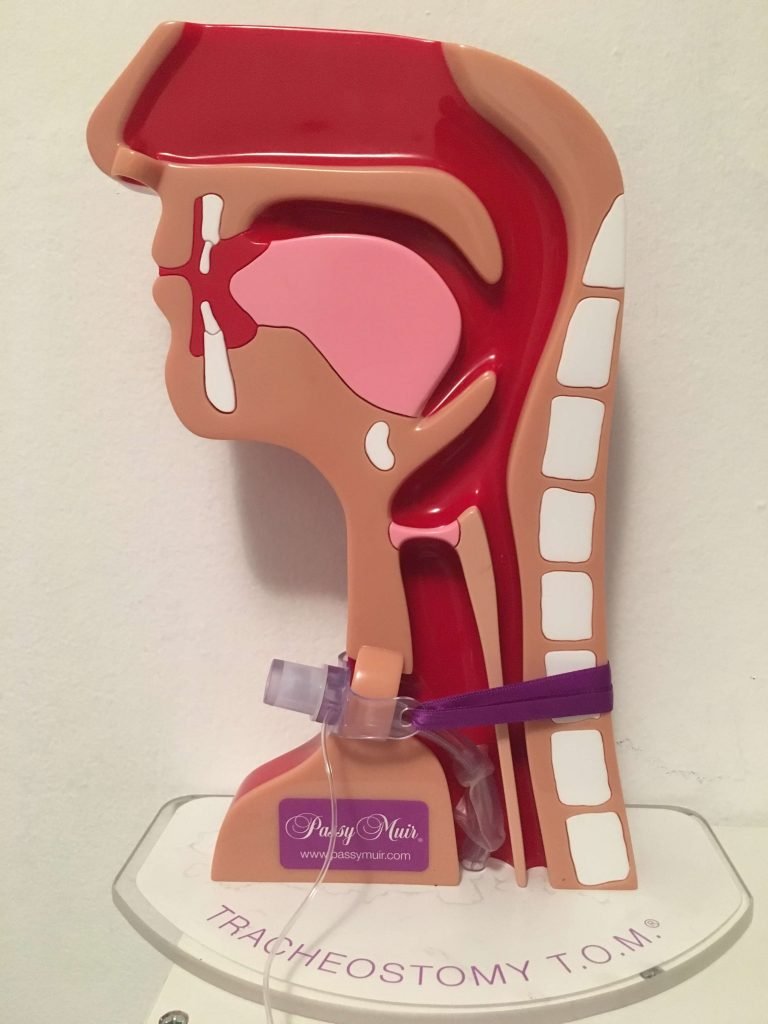
Respiratory therapists are also involved in providing the appropriate humidification, cuff management, and maintaining the skin surrounding the tracheostomy to prevent skin breakdown. RTs also often change the tracheostomy tube and inner cannula as needed. Patients are often evaluated by RTs for speaking valves in conjunction with a speech-language pathologist, particularly when a patient is on mechanical ventilation. RTs are also key role in assessing patients for decannulation.
Respiratory Therapy and Mechanical Ventilation
If the patient is on mechanical ventilation, the respiratory therapist will set up the ventilator settings in accordance to the physician’s orders. Some facility protocols allow for a therapist directed weaning protocol, which outlines certain parameters that the respiratory therapist may lower the ventilator settings to help wean a patient off mechanical ventilation. A respiratory therapist will attend to alarms and trouble shoot any reasons for the alarms. Some RTs take arterial blood gases and read and interpret the results.
Respiratory Therapy and Emergencies with Tracheostomy
Respiratory therapists are also vital for any emergency for patient’s with tracheostomy. RTs require critical thinking skills to determine why a patient may be in respiratory distress including accidental decannulation or tracheostomy tube misplacement. They perform CPR as needed. It is important to remember that patients with tracheostomy have two potential airways, one at the tracheostomy site and one through mouth and nose.
Emergency tracheostomy algorithm is located here through the Tracheostomy Safety Project in the UK.
Respiratory Therapists and Education
RTs may also be involved in education. When a patient with a tracheostomy tube is discharged home, the careproviders must be trained in basic tracheostomy management and emergency situations. Education can include check-lists for parents/caregivers, demonstration and return demonstration, tracheostomy simulation and emergency trach supply kit.
Respiratory Therapy and Decannulation
Once a tracheostomy tube is no longer required, decannulation can ensue. RTs are part of the team to provide input on decannulation. RTs may provide input on speaking valves, downsizing, cuffed or uncuffed tracheostomy tubes and capping readiness
Challenges for Respiratory Therapist and Tracheostomy
Some challenges that are faced by respiratory therapists are a lack of advanced education for respiratory therapists. There also may not be formal protocols on how to manage tracheostomy patients. Furthermore, at times the team that inserted the tracheostomy is not the current team managing the tracheostomy tube. Sometimes the managing party does not make decisions about removal unless that team inserted the tube.
Summary
Respiratory therapists are a very important part of the multidisciplinary team to care for a patient with tracheostomy. Multidisciplinary teams can include the physician, respiratory therapy, speech-language pathologists, clinical nurse specialist and physicial/occupational therapy. Several studies have shown decrease in ICU stay and increased speaking valve use with tracheostomy teams.
Resources:
Kalanuria AA, Ziai W, Mirski M. Ventilator-associated pneumonia in the ICU. Crit Care. 2014 Mar 18;18(2):208. doi: 10.1186/cc13775. Erratum in: Crit Care. 2016;20:29. Zai, Wendy [corrected to Ziai, Wendy]. PMID: 25029020; PMCID: PMC4056625.




Responses